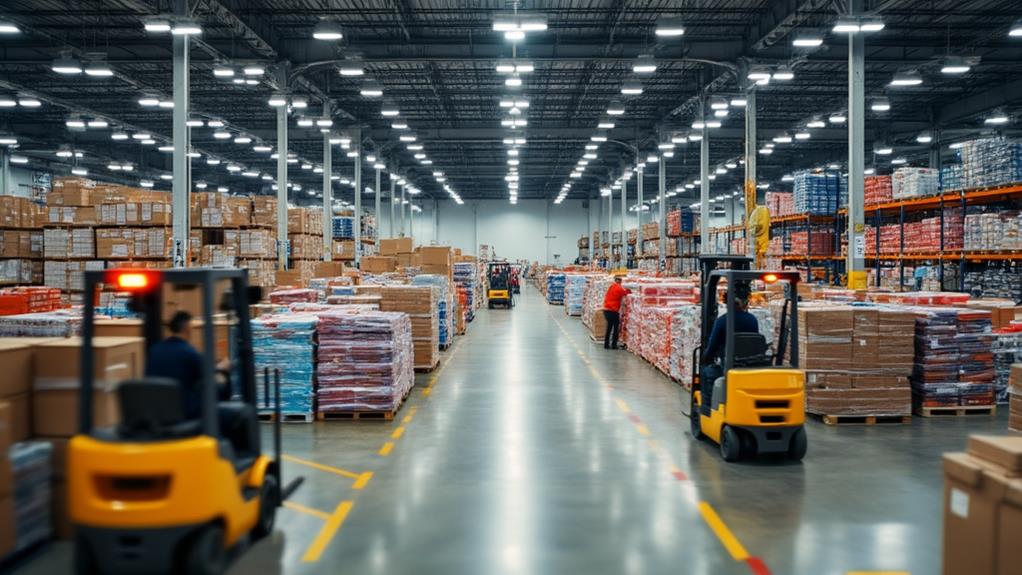
Wholesalers are essential, yet often unrecognized, players in the retail industry. They purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers at reduced prices, passing on savings that enable retailers to maintain competitive pricing. By managing inventory and optimizing delivery, wholesalers guarantee a seamless flow of products, from production to consumer sales. Their ability to store large inventories allows for quick replenishment, which is vital for retail operations. Specialization in specific product categories and diverse offerings guarantees that retailers can meet varied market demands. Understanding how wholesalers bridge the gap between producers and retailers can reveal their indispensable role in retail success.
Understanding Wholesaling Basics
Understanding wholesaling basics is vital for grasping the dynamics of the supply chain in the retail industry. Wholesaling involves purchasing bulk goods from manufacturers at discounted rates, a strategy that enables wholesalers to act as significant intermediaries between producers and retailers.
By acquiring large volumes of products, wholesalers can offer significant cost savings to retailers, who, in turn, mark up prices to reflect their operational costs. This model guarantees that retailers can maintain stocked shelves, ready to meet consumer demands.
Wholesalers' ability to buy in bulk not only provides financial advantages but also enhances inventory management capabilities for retailers. As a result, wholesaling is a pivotal component in guaranteeing the seamless flow of goods from production to final consumer purchase.
Key Roles in the Supply Chain
In the complex network of the retail industry, wholesalers occupy key roles within the supply chain that extend beyond mere intermediaries. By efficiently managing logistics and distribution, they play a crucial role in the seamless flow of goods.
Wholesalers bridge the gap between manufacturers and retailers, ensuring products are available in the right quantities and locations. Furthermore, they provide essential market insights and trends, aiding manufacturers in aligning production with demand.
Here are four key roles of wholesalers in the supply chain:
- Inventory Management: Wholesalers maintain large inventories to meet retailers' needs promptly.
- Bulk Purchasing: They negotiate bulk discounts, passing savings to retailers.
- Logistics Coordination: Wholesalers manage transportation and storage, optimizing delivery schedules.
- Market Analysis: They offer valuable market data to manufacturers.
Retailers' Dependence on Wholesalers
Despite the evolving landscape of retail, the dependence of retailers on wholesalers remains significant. Wholesalers serve as essential intermediaries, bridging the gap between manufacturers and retail outlets.
By purchasing goods in bulk, wholesalers provide retailers with access to a wide array of products at competitive prices, enabling retailers to maintain profitable margins despite fluctuating market conditions. This relationship is important for retailers who lack the resources to negotiate directly with manufacturers or manage large inventories.
Additionally, wholesalers offer logistical support, streamlining the process of procurement and delivery, which is fundamental for ensuring timely stock replenishment. As a result, retailers can focus on customer engagement and sales strategies, relying on wholesalers for a steady supply of diverse products.
Specialization and Market Diversity
Specialization in wholesaling plays a significant role in meeting the diverse needs of retailers and businesses. By specializing, wholesalers can offer tailored solutions that align with specific industry demands, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in supply chain management.
Market diversity is essential, as it allows wholesalers to cater to a broad spectrum of retail needs, from niche products to mainstream items. This adaptability is critical for sustaining competitive advantages in a dynamic market landscape.
Key benefits of specialization and market diversity include:
- Enhanced Expertise: Specialized wholesalers possess in-depth knowledge of specific product categories.
- Efficient Supply Chains: Streamlined processes reduce lead times and costs.
- Broader Product Range: Diverse offerings satisfy varied retailer demands.
- Targeted Solutions: Customization meets the unique needs of different market segments.
Comparing Wholesalers and Distributors
While both wholesalers and distributors play essential roles in the supply chain, their functions and relationships with manufacturers differ markedly.
Wholesalers purchase large quantities of goods from manufacturers, selling them to retailers without forming direct affiliations with producers. They often offer a variety of competing brands, focusing on bulk sales at discounted prices to manage inventory efficiently.
In contrast, distributors maintain exclusive agreements with manufacturers, granting them rights to sell specific products or brands. This direct relationship allows distributors to provide product support, technical knowledge, and specialized services.
Additionally, distributors often handle logistics and marketing efforts for manufacturers, ensuring products reach target markets effectively.
Consequently, although both entities facilitate product flow, their operational strategies and market engagements are distinct.